Last updated on December 27th, 2025 at 02:08 pm
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has earned its reputation as one of the most tax-friendly jurisdictions in the world. With no personal income tax and no capital gains tax on individuals, it has long been a haven for entrepreneurs, investors, and expatriates seeking financial efficiency.
But “no capital gains tax” doesn’t mean no tax system at all. With the introduction of corporate tax in 2023, and specific rules for real estate and cross-border investments, understanding the landscape is vital — especially for businesses operating in or from the UAE.
Here Arabian Vox explains what capital gains tax is, how it works globally, and how the UAE’s tax framework treats individuals, corporations, and foreign investors under the Federal Corporate Tax Law.

What Is Capital Gains Tax?
Capital Gains Tax (CGT) is a levy on the profit you make when you sell an asset that has increased in value! Whether it’s real estate, shares, a business, or investment funds. The tax applies only to the gain, the difference between the purchase price and the sale price.
In most countries, capital gains are split into two categories:
- Short-term gains: Profits on assets held for less than one year, usually taxed at higher rates.
- Long-term gains: Profits on assets held for more than one year, often taxed at a lower rate to encourage investment.
However, the UAE takes a unique position! No personal capital gains tax applies to individuals, and only corporate entities may be taxed on such profits under certain conditions.
No Capital Gains Tax for Individuals in the UAE
For individuals both UAE nationals or expatriates, there is no capital gains tax on personal investments.
This means you can sell your shares, property, or other assets without paying any UAE tax on the profit. There are also no inheritance or gift taxes, making the UAE highly attractive for wealth preservation and succession planning.
Key takeaway: If you’re not operating as a business, your capital gains are not taxed in the UAE..
However, remember that your home country’s laws still apply.
For example, U.S. citizens and residents of countries like India or the U.K. may still need to report and pay capital gains tax in their home jurisdiction, depending on tax residency and double taxation agreements (DTAs).
Corporate Capital Gains Under UAE Corporate Tax Law
While individuals remain exempt, corporate entities operating in the UAE are now subject to corporate tax, effective from June 2023.
The UAE Corporate Tax Law sets a 9% tax rate on taxable income above AED 375,000, aligning with global minimum tax standards while keeping the system competitive.
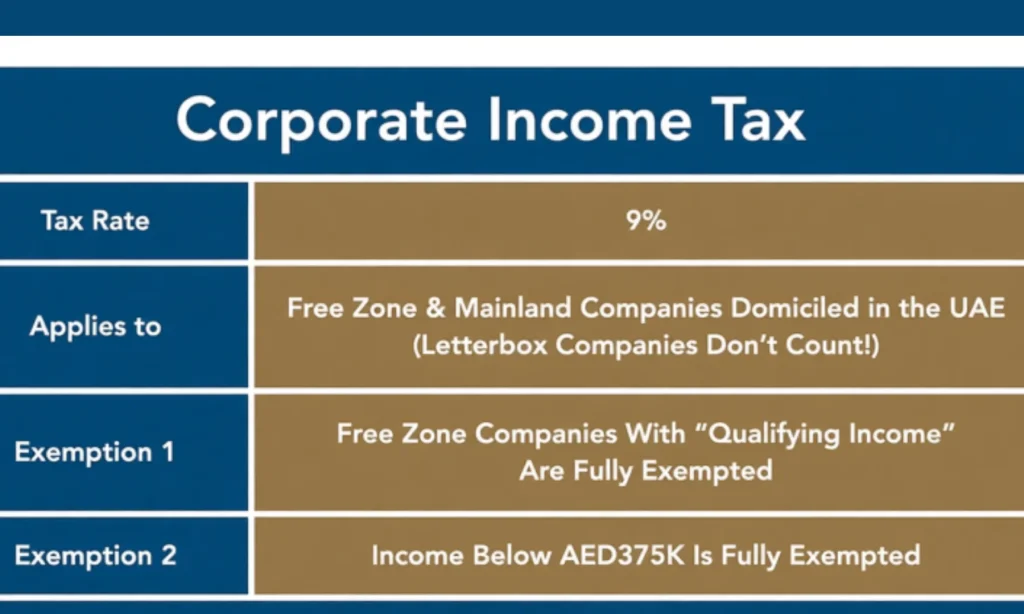
Corporate capital gains! Profits from selling shares, business assets, or subsidiaries may be considered part of taxable income unless they qualify for an exemption.
Corporate Tax Key Rates and Thresholds
- 0% on taxable profits up to AED 375,000
- 9% on profits above AED 375,000
- 15% (Domestic Minimum Top-up Tax) for multinationals with revenues exceeding EUR 750 million (OECD Pillar Two)
For complete guidance on how businesses can register, see our related article: How to register for corporate tax in the UAE.
The Participation Exemption: When Capital Gains Are Tax-Free for Companies
The participation exemption (Article 23 of the Corporate Tax Law) is one of the most investor-friendly provisions in the UAE. It allows companies to exclude capital gains and dividends from taxable income when specific conditions are met.
To qualify, a company must:
- Hold at least 5% ownership in another entity (the “Participating Interest”).
- Have held or intend to hold this interest for at least 12 months.
- Ensure the subsidiary is subject to tax in its jurisdiction at a minimum rate (usually 9% or more).
- Not claim a tax deduction for any impairment losses or write-downs related to the investment.
When these conditions are satisfied, dividends and capital gains from that investment are entirely exempt from corporate tax.
Capital Gains on Real Estate in the UAE
Real estate is one of the UAE’s most popular investment assets, and its treatment is straightforward:
For Individuals
There’s no capital gains tax on the sale of property, whether residential or commercial.
However, there are transaction-related fees:
- Dubai: 4% transfer (registration) fee payable to the Dubai Land Department
- Abu Dhabi: 2% transfer fee
- Municipality fees: Typically 5% of annual rental value
These are administrative costs, not income taxes.
For Companies
If property transactions are part of a business activity (for example, real estate development or leasing), the gains are included in taxable income and subject to the 9% corporate tax — unless the participation exemption applies through a holding structure.
Capital Gains on Shares and Securities
For Individuals
Profits from selling listed or unlisted shares, bonds, or mutual funds are not taxed in the UAE. This rule applies equally to residents, expatriates, and foreign investors who trade through UAE platforms.
For Corporations
Capital gains from share disposals may be taxed as part of ordinary profits.
However, if the company meets the participation exemption conditions, those gains are excluded from taxation.
This makes the UAE especially favorable for holding companies, private equity structures, and venture capital exits. Find more tax explanations in the Finance category.
Free Zones and Capital Gains Tax Benefits
Free zones remain one of the cornerstones of the UAE’s tax system.
Entities that qualify as “Qualifying Free Zone Persons” (QFZP) may enjoy a 0% corporate tax rate on qualifying income, provided they meet substance and compliance requirements.
Capital gains from qualifying activities (e.g., share disposals, intra-group transfers) may therefore be tax-free under the free zone regime.
However, if a free-zone company earns non-qualifying income, the 9% standard rate applies. For global comparison, check tax rules in the US or Philippine travel tax.
Withholding Tax: The UAE’s Zero-Rate Advantage
Under Article 45 of the Corporate Tax Law, withholding tax applies to specific UAE-sourced income paid to non-residents.
But — and this is crucial — the current rate is 0%.
This means no tax is withheld on payments such as:
- Dividends
- Interest
- Royalties
- Capital gains
For foreign investors, this zero-rate environment ensures uninterrupted capital repatriation and adds to the UAE’s investment appeal.
You can read more about the concept in our related article: what is withholding tax
Double Taxation Agreements and International Considerations
The UAE has signed more than 140 Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs) with countries worldwide.
These treaties prevent the same income from being taxed twice! Once in the UAE and again in your home country.
For instance:
- Indian residents in the UAE can benefit from the India-UAE DTAA, which may prevent double taxation on capital gains.
- US citizens, however, remain subject to US tax on their global income under citizenship-based taxation.
- UK residents must report worldwide gains but may get credit for taxes paid elsewhere.
If you’re an expatriate or investor, securing a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC) from the UAE can help you prove UAE residency and benefit from treaty relief.
How Real Estate and Share Gains Differ in Tax Treatment
|
Asset Type |
Individual |
Corporate |
Notes |
|
Real Estate |
No CGT, but 2–4% transfer fee |
Taxable if part of business |
Free zones may reduce or exempt |
|
Shares |
No CGT |
Taxable unless exempt |
Participation exemption applies |
|
Foreign Assets |
No UAE tax |
Taxable if business-related |
Treaty relief may apply |
Compliance Checklist for Businesses
If your company could realize a capital gain, review this compliance roadmap:
- Identify who is selling — an individual, a mainland company, or a free zone entity.
- Confirm your registration with the FTA. (If not yet registered, see how to register for corporate tax in uae).
- Test participation exemption eligibility.
- Verify free zone qualification (if applicable).
- Maintain documentation (share registers, board minutes, valuations).
- Account for transaction fees, such as land transfer charges.
- Review DTA implications to avoid double taxation abroad.
- File corporate tax returns accurately and on time.
Tip: Companies must obtain a Tax Identification Number (TIN) when registering for UAE corporate tax. Learn more about what is tax identification number.
UAE vs. Other Countries: A Comparative Snapshot
|
Country |
Personal CGT |
Corporate CGT |
Notes |
|
UAE |
❌ None |
✅ 9% (with exemptions) |
Investor-friendly environment |
|
UK |
✅ Up to 20% |
✅ 25% |
Based on residency |
|
US |
✅ 0–20% |
✅ 21% |
Worldwide taxation for citizens |
|
India |
✅ 10–20% |
✅ 25–30% |
DTA with the UAE provides some relief |
|
Philippines |
✅ 15% |
✅ 30% |
Plus other taxes, such as the Philippine travel tax |
The UAE’s 0% personal CGT and competitive corporate framework make it one of the most favourable global jurisdictions for investors and entrepreneurs.

FAQs
Is there a capital gains tax for individuals in the UAE?
No. Individuals in the UAE do not pay CGT on the sale of assets like shares or property.
Are corporate capital gains taxable?
Yes, they are part of corporate taxable income unless exempt under the participation exemption.
Does selling real estate trigger tax?
Only transaction fees (2–4% transfer fees) apply, not capital gains tax.
What is the corporate tax rate in the UAE?
9% for business profits exceeding AED 375,000. Read: what is corporate tax.
Are free zone companies exempt from capital gains tax?
Yes, if the gains qualify as “qualifying income” under FTA regulations.
Are there taxes on foreign share sales?
Not in the UAE, but foreign tax may apply depending on your residence and treaty position.



